3 Ways Smoking Increases Dental Implant Complications
- By Admin
- •
- 11 Oct, 2018
- •

Dental implant surgery is one of the most successful procedures in all of restorative dentistry, with about 98percent of patients experiencing healthy, long-lasting results.
Unfortunately, smokers are far more likely to be within the 2 percent of patients who do experience problems, even in dental implant procedures. Here are three ways smoking increases dental implant complications, and why you should quit now.
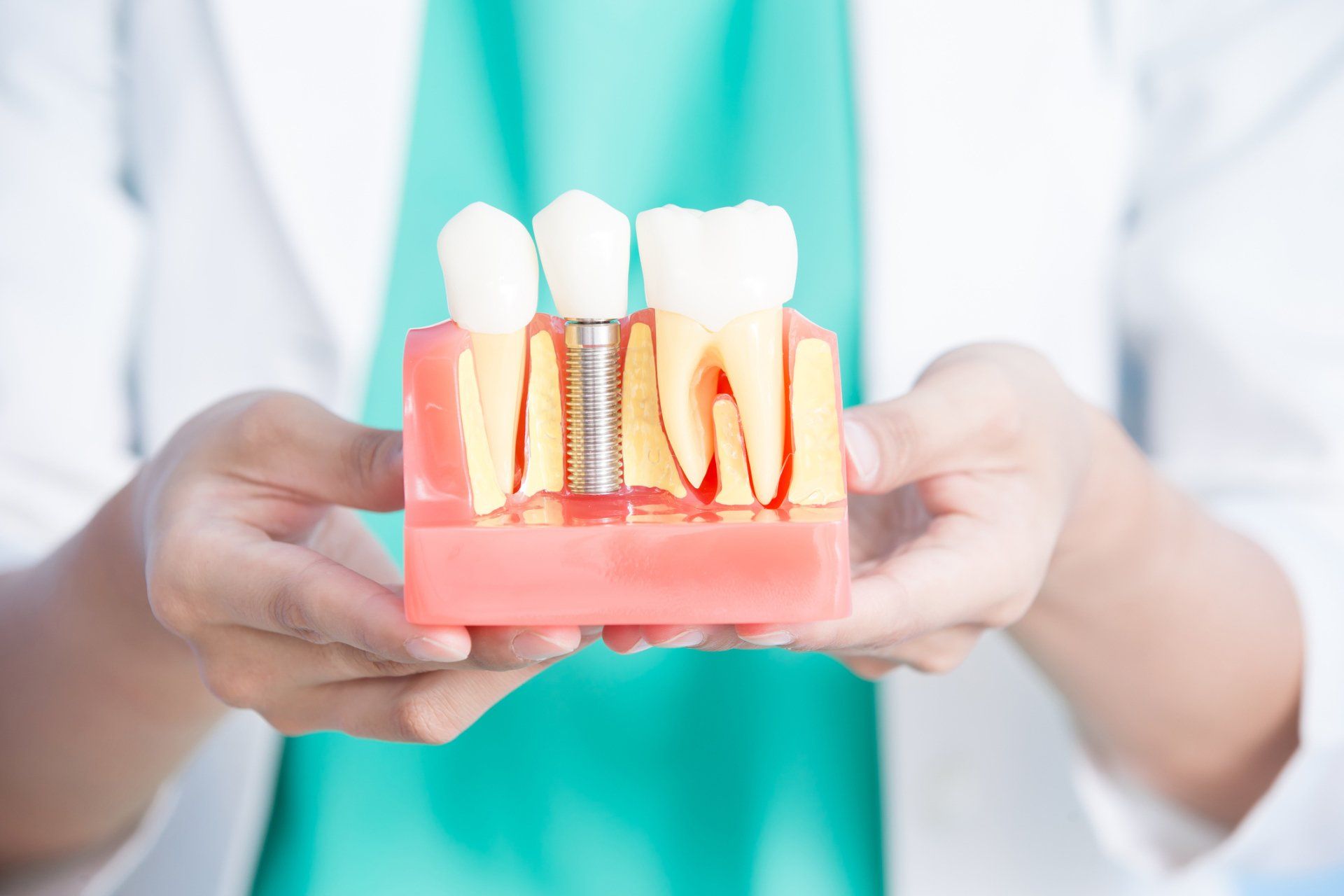
1. Impacting Osseointegration
Dental implants gain their support from small titanium posts that are placed in your natural jaw tissue. Under healthy circumstances, these posts actually fuse with the existing bone in a process called osseointegration. After this connection is created, the posts become a strong, stable anchoring point for permanent crowns.
Unfortunately, the chemicals and pollutants introduced by cigarette smoke can slow down integration, making implants more likely to fail. Cigarette smoke contains more than 7,000 chemicals, 69 of which are poisonous or known to cause cancer.
When you smoke, the highly vascular tissues inside of your mouth can absorb these chemicals, and to protect themselves, the vessels start to close off. Unfortunately, this circulation issue also makes it more difficult for your dental implants to heal properly.
To prevent problems with osseointegration, dentists recommend stopping smoking altogether to lower your complication rates. Ideally, patients should stop smoking a few months before implants are placed, giving their smile the chance to become healthier before undergoing oral surgery.
2. Thickening Oral Tissues
When you smoke, you are inhaling smoke from a tiny fire lit at the end of a cigarette. Although it might seem insignificant, the embers at the tip of a cigarette can get very hot between drags, significantly increasing the temperature inside your mouth. While most people don't worry too much about this hot smoke, it can actually damage the tissues inside of your mouth, making them thicker.
As you smoke, this hot vapor physically burns the tissues inside of your mouth, damaging your mucosa on a molecular level. As tissues scar and thicken, they can block off salivary flow, making your mouth drier. Unfortunately, saliva plays several important roles inside of the mouth, including neutralizing bacterial acids and rinsing away food particulates.
In addition to causing bad breath, this new mouth dryness also exacerbates oral decay and infections, putting your new implants at risk. Although dental implants themselves are immune to cavities, implants rely on a healthy mouth to heal properly and remain comfortable. If you have neighboring teeth that develop decay, the infections can travel to nearby areas, affecting the stability of your implants.
3. Reducing Gum Tissue Resilience
In addition to impacting the thickness and healing ability of oral tissues, smoking can actually make gum tissue more likely to break down, contributing to dental sensitivity, exposed dental implants, and even periodontal disease.
Healthy people have protective cells called neutrophils present in their gum tissue to protect against periodontal disease. While smokers also have neutrophils, their numbers of these protective cells are much lower, while their quantities of harmful hormones and chemicals like MMPs, interleukin-1, elastase, and prostaglandin-2 are higher.
As a result, smokers are much more likely to suffer from tissue breakdown, damaging inflammation, loss of collagen, and even bone resorption than non-smokers, making periodontal disease more severe. However, by stopping smoking, you can improve the immune response in your gum tissue, protecting against a disease that could destroy your implant connections and your remaining teeth.
If you are considering dental implants and you are a smoker, stop by and visit us here at Premier Dentures and Implants. In addition to helping each patient to assess their personal level of risk, we focus on creating a comfortable, safe environment where people can access an excellent level of dental care. Stop by and see us today to learn more.